If this happens, the fix isn’t too difficult. You can use your Linux distribution’s terminal app or use GUI tools to fix the problem. By following the steps below, you should have your disk mounted in Linux in no time. If you have an unmounted disk that you need to use, then here’s how to mount a disk in Linux.
How to Mount a Disk in Linux Using the Disks Utility
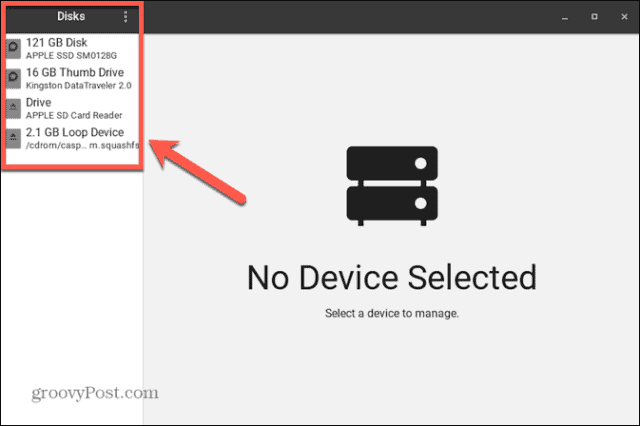
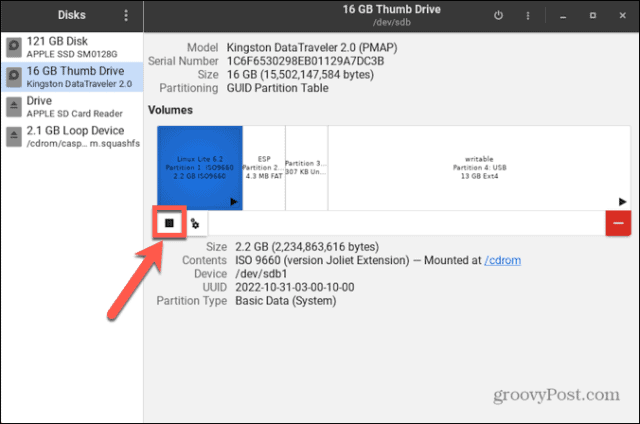
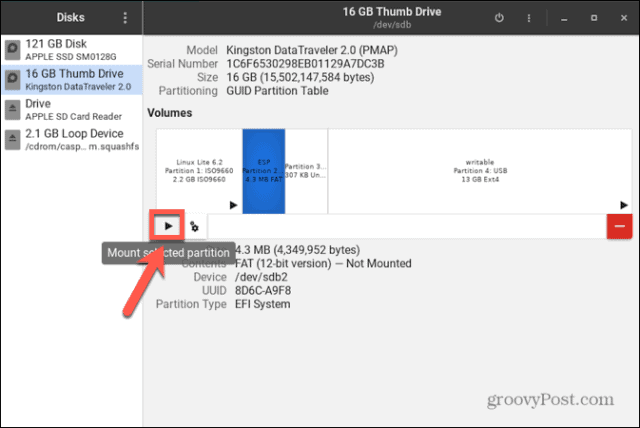
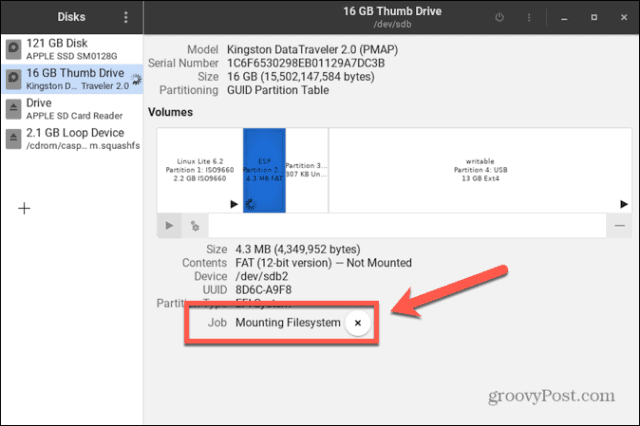
If your disk hasn’t been mounted, you can use the GNOME Disks utility to mount or unmount it (if your distribution has it installed). This allows you to see all of the disks connected to your computer. You can also perform actions on the drive, such as mounting and un-mounting, creating partitions, and repairing the file system. These instructions should work for most Linux distributions with a GUI. To mount a disk in Linux using the GNOME Disks utility:
How to Mount a Disk in Linux using Terminal
It’s also possible to use the Linux terminal to mount a disk in Linux. In order to do so you’ll first need to identify the disk you want to mount, then create a directory for the disk to mount to. You’ll then be able to mount the disk using the Mount command.
How to Identify the Disk in Terminal
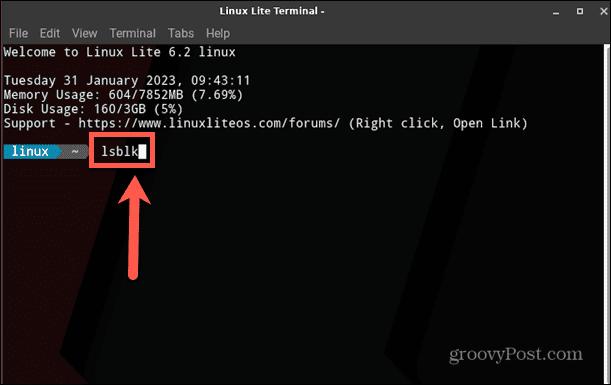
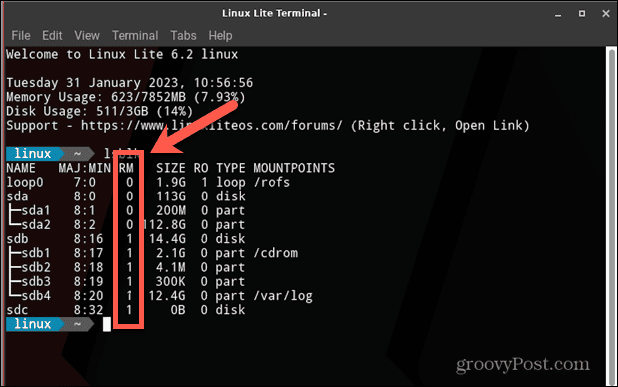
In the terminal, you can use a command to list all available block devices. These represent devices connected to your computer, including any disks. With a little detective work, you can find the block device that represents the disk you want to mount. To identify your disk in the Linux terminal:
How to Create a Specific Directory to Mount the Disk
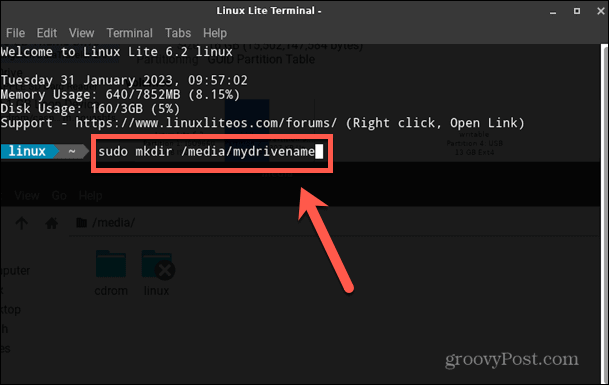
When you plug in a new USB drive, it will usually be mounted in the Media directory. If you would prefer to mount your drive to a specific directory, you can create one in Terminal. To create a directory in the Linux terminal:
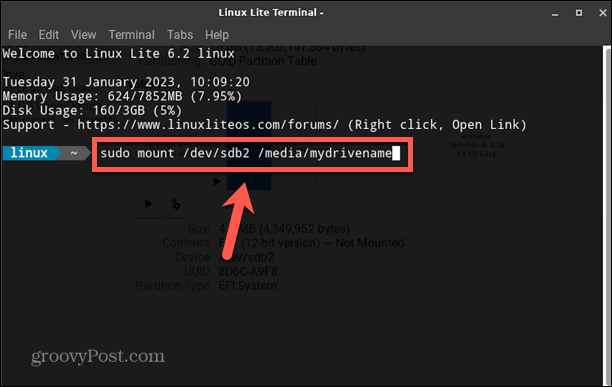
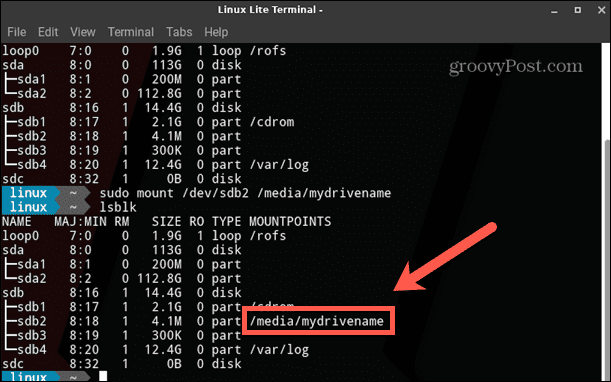
How to Mount the Disk Using the Mount Command
Once you know the block device name for your drive and have created the directory you want to mount it to, you’re ready to mount your disk. You can use the Mount command to do so. To mount a disk using the Mount command:
Becoming a Linux Power User
Learning how to mount a disk in Linux is just one way to take more control of your Linux system. There are plenty of other tips and techniques that can help you on your way to becoming a Linux power user. For example, you can learn how to securely delete files in Linux to ensure that all of the data is completely removed from your system. You can also learn how to empty a file in Linux if you have large files that are taking up a lot of space. And if you want to configure your system, you can learn how to set environmental variables in Linux. Comment Name * Email *
Δ Save my name and email and send me emails as new comments are made to this post.
![]()